Explore Operations Management
Operations Management Courses and Lessons
The Study.com library of engaging online business courses touches on operations management topics including production operations management and operations and systems.
Explore our full library of operations management courses:
Operations Management
Business 121: Introduction to Entrepreneurship
Business 312: Advanced Operations Management
Retail Operations
Business Development Training
Explore our full library of operations management courses:
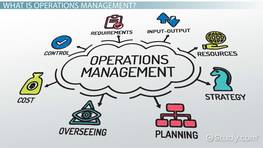
What is Operations Management?
Operations management can be defined as a field of business and industry that deals with the administration of business practices to increase the efficiency of a business organization as much as possible. This field includes the planning and organizing of what goes in and out of an organization. For example, an operations manager oftentimes oversees the organization's inputs (what goes in) like materials, technologies, and labor, and converts them into outputs like services and goods (what goes out). The goal is to balance the revenues and costs as much as possible in order for the organization to increase its profit (gains).
There are five basic principles of operations management:
- planning,
- organizing,
- leading,
- staffing, and
- controlling.
Planning is essential in management. It involves choosing appropriate goals, the strategies to use, the actions to take, and understanding the limitations and resources that are needed. Organization is essential as all the principles are connected and should work together towards the same goal. Managed passion refers to the motivation of operational management employees which ultimately helps the organization to succeed. Leading requires effective communication skills and involves setting clear goals and motivating employees. Leaders should be humble which includes understanding the limitations which will help the organization save money in the long term. Staffing involves selecting the employees for the organization and the right staff will help the organization meet its goals. Controlling involves improving performance and taking action.
The success of operations management includes the interest of the customer because when the customers are happy, they will keep going back to the organization. Fundamentals are also important and it refers to keeping 80% of what is working for the organization while changing the other 20% to try new techniques. Varying techniques and processes can increase the creativity and productivity of an organization while being open to change can lead to a successful company.